Fighting Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases:
A major challenge of the 21th century.

of the world’s population
≈ 460M patients;
700M in 2040

of the French population
≈ 3.5M patients
+ 1M undiagnosed

of the local population
the highest prevalence in France
- Major cause of blindness, end stage kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, amputations, …
- 6 years less life expectancy for people with diabetes
- Worldwide: ≈ 4M deaths per year; overall cost ≈ 800 billion dollars in 2019;
- In France: 70,000 hospitalizations per year; 15% of public health expenditure (10 billion euros per year)
Diabetes, impaired blood sugar control
Diabetes is a disease characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, that is, excess sugar in the blood and therefore too high a level of glucose (blood sugar). It is diagnosed when fasting blood sugar, measured twice, is greater than 1.26 grams of glucose per liter of blood.
Blood sugar control is a dynamic process that adjusts blood sugar levels throughout the day based on the body’s energy demand and food intake. This control is mainly carried out by the pancreas, an organ which detects variations in blood sugar levels thanks to two types of cells grouped together in cell clusters called islets of langerhans :
- Pancreatic β (beta) cells secreting insulin, a hypoglycaemic hormone that induces a signal throughout the body to capture blood glucose to the body’s cells: muscle, adipose tissue and liver where it will be transformed and stored .
- Pancreatic α (alpha) cells secreting glucagon, a hyperglycemic hormone which acts mainly on the liver by causing glycogenolysis and the release of glucose in the blood.
In people with diabetes, this regulatory system is altered, causing problems in the absorption, use and storage of sugars from food. This results in chronic hyperglycemia (constantly high blood glucose levels).
There are two major types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes
formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes (IDD), affects about 10% of people with diabetes and is usually discovered in young people: children, adolescents or young adults.
Type 2 diabetes
which affects about 90% of people with diabetes and usually occurs in people over 40 years old. However, the first cases of adolescents and young adults affected appear in France.
In addition to these two major types, there is also so-called gestational diabetes which occurs in pregnant women towards the end of the 2nd trimester. It can last the time of pregnancy or be indicative of previous diabetes.
NOUVEAU
Découvrez notre blog consacré
aux mille et une facettes du diabète.
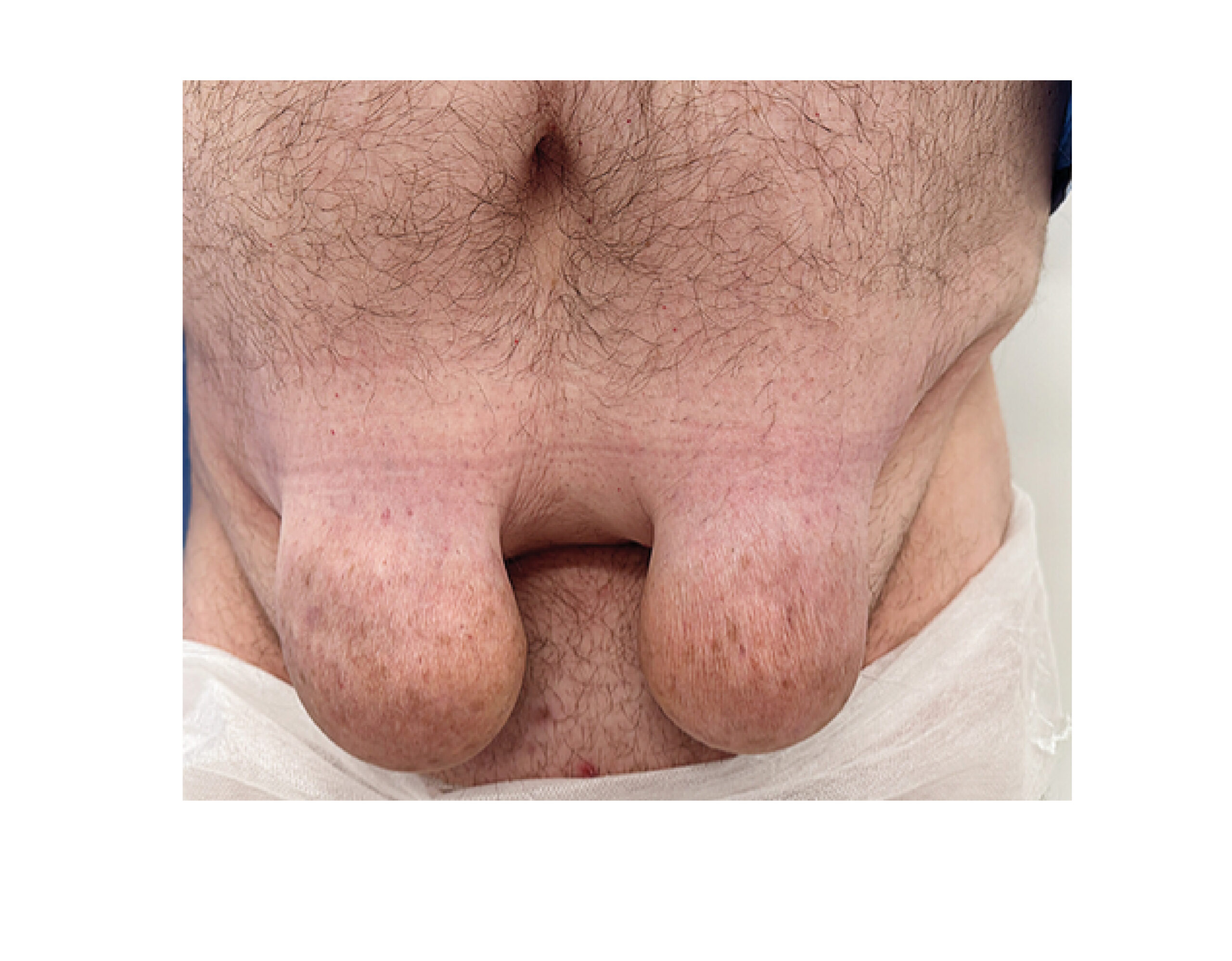
Publié le 26/06/2025 par Marc Gozlan
Amyloïdose cutanée localisée : une complication rare des injections d’insuline chez les personnes diabétiques
Diabète de type 1

Publié le 11/06/2025 par Marc Gozlan
Diabète de type 2 et muscle squelettique : décryptage de signatures moléculaires de l’insulinorésistance
Diabète de type 2
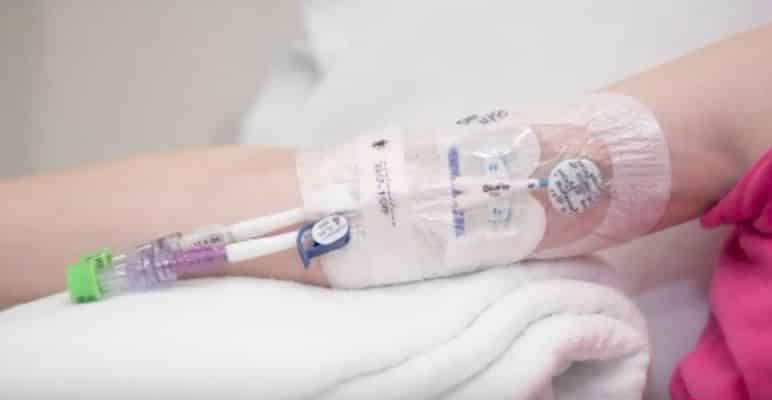
Publié le 26/05/2025 par Marc Gozlan
Acidocétose diabétique de l’enfant : des cas de thrombose associée à la mise en place d’un cathéter dans une veine profonde
Diabète de type 1
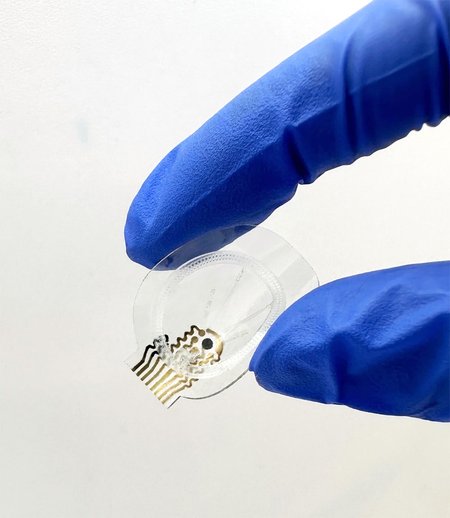
Publié le 06/05/2025 par Marc Gozlan
Plaies chroniques diabétiques : un pansement intelligent pour surveiller l’exsudat en continu
Diabète de type 1




